The term “percent” means “for every hundred”. This term percent is generated from the Latin word Centum which means hundred. So, in percentage problems, one has to calculate the required value for every hundred units. For example, 20% means 20 out of 100. This is a fraction and is denoted by 20/100 or 0.20. So percent is basically a form of a fraction that is denoted by the usual fraction or decimal fraction. The symbol “%” is used to imply the abbreviation of percent or percentage. The percentage is a ratio that is expressed using a denominator of 100.
The symbol of percentage known as percent sign has been evolved from the Italian term “per cento” which means “for a hundred”. In British English, the percent is usually written as two words (per cent), But in American English, percent as one word is the most common variant.
The mathematical term percentage is widely used. It is quite easier to comprehend a value if it is provided in percent form. The major applications of percentage are found in:
- Interest rates.
- Percentage increase or decrease of any value.
- Taxes
- Making comparisons
- Examination test marks
- Discount Sales
Percentage Calculation Formula or Rules
There are various rules of formulas for percent calculation depending on the type of the actual percentage problem or worksheet. Some of the specific rules for percentage calculation are provided below:
Rule 1: The most general formula for calculating the percentage is:
Percentage=(Value/Total Value) X 100.
For example, if in an examination 20 out of 25 students pass the exam, Then the percentage of students passing the exam={(value, 20)/ (Total Value, 25)} X 100= 20X100/25=80%.
Rule 2: Percentage increase in calculated using the following formula:
Percentage Increase= (Increased Value-Original value)/Original value X 100 = (Actual increase/Original) X 100
For example, if the population of a village in the year 2019 is 1000 and in the year 2020 is 1200. Then the percentage increase of population in that period can be calculated as: {(Increased value, 1200-original vale, 1000)/(original value, 1000)}X100={(1200-1000)/1000}X100=200X100/1000=20%.
Rule 3: Similarly, Percentage decrease is calculated using the following formula:
Percentage Decrease= (Original value-Decreased Value)/Original Value X 100 = (Actual decrease/Original) X 100
For example, if the price of a pen in the month of June was $10 and the same is available in July for $8. Then the percentage decrease is: {(10-8)/10}*100=20%
Rule 4: The total of all part percentages is always equal to 100%. So, if only one part is unknown that can easily be calculated by deducting the total of known percentages from 100%
For example, if in a class there are 30 boys and 20 girls. then the percentage of boys=(30/50)X100=60% and the percentage of girls=(20/50)X100=40%. Total percentage=60%+40%=100%. So in this problem, we can easily calculate the percentage of girls by deducting 60 from 100.
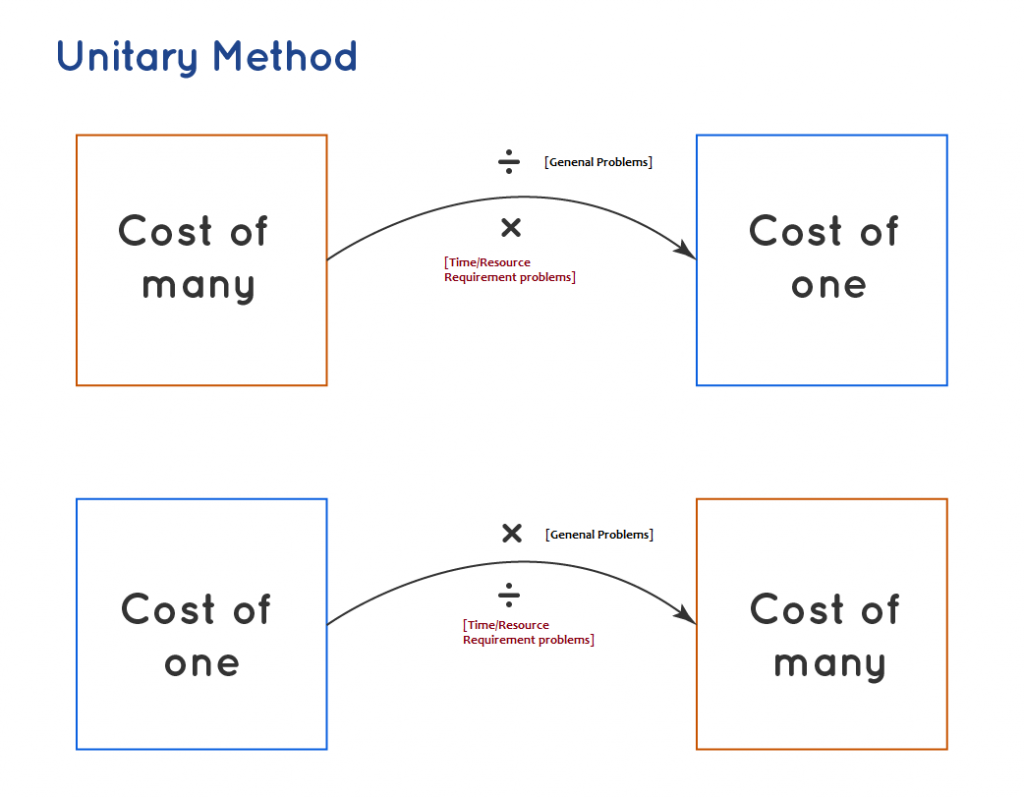
Rule 5: Use the unitary method to calculate the required percentage. In the unitary method, we already calculate the value for 1 unit. So, we can simply multiply that value by 100 to get the required percentage.
Percent Worksheets for Practising
Q1. Convert the following fractions into percent rates.
- 1/4
- 0.20
- 1/20
- 3/5
- 1.25
Q2. Convert the following percentages into fractions and decimals.
- 8%
- 56%
- 16%
- 150%
- 12%
Q3. What is the meaning of 100%?
Q4. Calculate the values of the following percentages.
- 10% of $500
- 20% of 30 m 50 cm.
- 40% of 150 Tonne.
- 9% of Rs 900.
- 38% of 250 liter.
Q5. Calculate the percentage value of the following
- 20 out of 50
- 50 m out of 50 kilometer.
- 75 cents out of $50.
- 15 cm out of 150 m.
- 15 kg out of 30 quintal.
Q6. Percent Worksheet Word Problems
- A fruitseller gained 25% by selling 30 Kg of guava for Rs 3000. So, what is the original price of each Kg of guava?
- A book costing $25 is sold for $20 in an online shopping site. So, what is the offer percentage on that online site?
- What is the sum of money of which 25% is $50?
- Ram sold his pen to Shyam for $25 and gained 25%. What is the cost price of the pen?
- Swarnali has 10 chocolates which she bought for Rs 20. She wants to sell those at a profit of 25%. She sold 3 chololates to Sumita at Rs 10. How much she should get by selling the remaining chocolates to fulfill her wish?
- In a garden with 1200 trees, 40% are fruit trees; So what is the number of trees of other kinds?
- A toy seller purchased a lot of 50 toys for $25 and expects a profit of 20% on this. He found that 10% toys are broken in the lot. So at what price he should sell each toy to fullfill his expectation?